Somalia Zimbabwe Tuberculosis Malnutrition Sri Lanka
Democratic Republic of Congo Colombia Myanmar Central African Republic Chechnya
View The "Top Ten" Slideshow, Press Release, and Media Coverage.
Displaced Fleeing War in Somalia Face Humanitarian Crisis

Somalia 2007 © Jehad Nga
Tens of thousands of Somalis are living in camps like this one, north of the capital Mogadishu, suffering from a lack of water, food, shelter, and access to medical treatment.
As violence in Somalia escalated this year to some of the worst levels in over 15 years, both assistance for and attention to one of the most challenging and acute humanitarian situations in the world seemed to wane. Ethiopian troops and Transitional Federal Government forces, supported by international partners such as the United States and the European Union, clashed with a range of armed groups, including remnants of the Islamic Courts Union. The fighting caused an unknown number of civilian casualties and the displacement of hundreds of thousands of people from the capital, Mogadishu.
In 2007, MSF increased its presence in Mogadishu in different locations and opened an emergency response program in Afgooye, just outside the capital, where an estimated 200,000 internally displaced persons sought refuge, living in extremely harsh conditions with little access to food, water, and shelter. Many of those remaining in Mogadishu are staying in makeshift camps with little more than ripped cloth and plastic sheeting for shelter and are exposed to a high degree of violence.
In a country where a 16-year conflict has resulted in some of the world's worst health indicators, with an estimated life expectancy of 47 years, few international aid organizations managed to run effective independent aid programs. Present since 1991, MSF increased its operations in 2007 and is now running projects in 10 out of the 11 regions of south and central Somalia. Nevertheless in many areas, especially in the Mogadishu area, MSF is extremely frustrated by its inability to reach more patients due to security concerns.
In August, MSF called upon all parties to the conflict to respect the safety of medical workers and allow access to medical care in and around Mogadishu. Throughout MSF hospitals, from Kismayo to Galcayo, the medical services provided range from primary and maternal to surgical care, with nurses and doctors treating malnutrition, tuberculosis, kala azar, cholera, and war-related trauma on a daily basis.
Political and Economic Turmoil Sparks Health-Care Crisis in Zimbabwe

Zimbabwe 2007 © Dirk-Jan Visser
Women queue to collect water from a spring outside the capital city of Harare. Zimbabweans, especially those in high-density areas, are facing massive water shortages.
Rampant unemployment, skyrocketing inflation, food shortages, and political instability continued to wrack Zimbabwe in 2007. Up to 3 million people are believed to have fled to neighboring countries in recent years among a population of 12 million.
The national health-care system, once viewed as one of the strongest in southern Africa, now threatens to collapse under the weight of this political and economic turmoil with the most acute consequences potentially for the estimated 1.8 million Zimbabweans living with HIV/AIDS. Currently, less than one-fourth of the people in urgent need of life-extending antiretroviral (ARV) treatment receive it. This translates into an average of 3,000 deaths every week. And the prospects for a further scale up of the national AIDS program are dim.
Trained medical professionals are leaving the country, the government program for HIV/AIDS treatment is oversubscribed, and the lack of ARV supplies has stifled further expansion. Patients often face obstacles to reach hospitals or clinics because of high fuel and transport prices.
Through programs in Bulawayo, Tshlotsho, Gweru, Epworth, and various locations in Manicaland province, MSF provides free medical care to 33,000 people living with HIV/AIDS, 12,000 of whom are receiving ARV treatment—nearly one tenth of all people on treatment. However, MSF's ability to care for more people in need is hindered by the lack of trained health workers, restrictions on which staff can prescribe ARV drugs, and stricter administrative requirements for international staff to work in the country.
At the same time, Zimbabweans are feeling the health impact of degraded or nonexistent water-and-sanitation systems. During the year, outbreaks of diarrhea affected people living in the capital, Harare, and Bulawayo, the second largest city. Fleeing the country is also a dangerous enterprise as evidenced by the reports of refugees being beaten and raped along the South African border, and those who do make it across may be destined to live in the shadows with little or no access to health care.
Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Spreads As New Drugs Go Untested
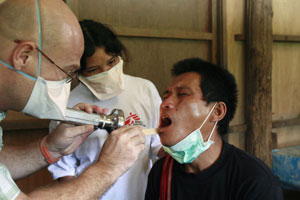
Thailand 2007 © Francesca Di Bonito
A MSF physician examines a tuberculosis patient in the Maela refugee camp near Maesot.
Every year, tuberculosis (TB) kills an estimated two million people and another nine million develop the disease. In spite of the rising human toll, there have been no advances in treatment since the 1960s and the most commonly used diagnostic test—sputum smear microscopy—was developed in 1882 and only detects TB in half of the cases. An estimated $900 million is needed annually for research and development for TB, but only $206 million is invested worldwide.
Existing treatments and diagnostics are even less adapted for people living with HIV/AIDS, the easiest prey for the TB bacilli. And for those who become infected with multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB)—more than 450,000 people every year—or develop it as a result of incomplete treatment, the prospects for survival are even bleaker. The only guarantee for the few who are able to access treatment for MDR-TB is up to 24 months of ingesting a daily cocktail of highly toxic and expensive drugs that often trigger violent side effects.
In MSF programs in Armenia, Abkhazia, Georgia, Cambodia, Kenya, Thailand, Uganda, and Uzbekistan, even under the best conditions, only 55 percent of MDR-TB patients completed the 18 to 24 month treatment. The remaining proportion died, did not improve, or stopped treatment altogether because of side effects.
Adding to the frustration for medical staff on the TB pandemic's front line is the fact that not all new drugs are being tested in the neediest patients—those with MDR-TB. A recent article authored by international experts and published in the open-source medical journal PLoS Medicine, called for the testing of new drugs in patients whose TB is resistant to standard treatment. This approach could make it easier to detect anti-TB activity of new drugs and ultimately accelerate drug development.
Expanded Use of Nutrient Dense Ready-to-Use Foods Crucial for Reducing Childhood Malnutrition

Niger 2007 © Anne Yzebe/MSF
Mothers feed their children a ready-to-use food (RUF) product called Plumpy'Doz at an MSF outpatient nutrition center in Maradi.
Acute malnutrition in early childhood is common in large areas of the Horn of Africa, the Sahel, and South Asia—the world's “malnutrition hotspots.” Every year, malnutrition is associated with the deaths of five million children under the age of five.
Recently, an effective response has emerged in the form of nutrient dense ready-to-use foods (RUFs) that can save the lives of acutely malnourished children. These products come in the form of milk- and peanut-based pastes enriched with all the vitamins and nutrients needed for rapid recovery. And they do not require refrigeration or preparation, allowing most malnourished children to be treated with RUF at home. But so far these products are only available to a tiny fraction of the severely malnourished children who need them.
MSF urges international donors to support systematic purchasing and use of RUF in countries where it's needed. RUF also has the potential to prevent children from becoming acutely malnourished by treating at earlier stages. This means international food aid programs targeting young children must incorporate RUFs to treat less severe forms of malnutrition and to prevent acute malnutrition from developing in areas of high prevalence.
In Niger in 2007, MSF launched a pilot program using a modified RUF as a supplement to prevent some 62,000 children from becoming malnourished during the period of seasonal food shortages. The program has helped to stanch a rise in acute malnutrition in one of the country's high prevalence districts.
In addition to calling for urgent scale up of RUF for children most in need, MSF is urging further efforts to use supplemental RUF to prevent children from becoming dangerously malnourished in the first place.
Civilians Increasingly Under Fire in Sri Lankan Conflict
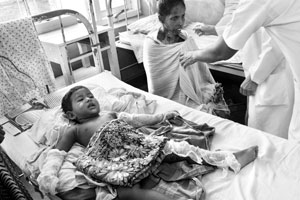
Sri Lanka 2007 © Henk Braam
A wounded woman and child receive treatment at MSF's surgical program in Vavuniya, a town close to the front lines of the ongoing conflict between government and rebel forces.
Caught in the middle of fighting between government forces and the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eeelam (LTTE), civilians in Sri Lanka's eastern and northern regions live in terror. Sri Lanka has been in the grips of this fighting on and off for nearly 25 years, but the conflict has received very little attention, especially in terms of the toll it has taken on civilians living in the conflict zone.
Targeted bombings, killings, mine attacks, suicide bombings, abductions, forced recruitment, extortion, restrictions on movement, and arbitrary arrests make day-to-day life in Sri Lanka increasingly precarious. Hundreds of thousands of Sri Lankans in need of humanitarian assistance have been displaced since the resumption of major fighting in August 2006.
The dire nature of the situation is compounded by a general climate of hostility and suspicion toward humanitarian aid organizations. As a result, humanitarian aid is increasingly restricted and civilians suffer from the resulting lack of access to lifesaving emergency assistance. This lack of respect for humanitarian aid comes at a time when areas near the front line of fighting have lost nearly all of their medical specialists and hospitals no longer have the human resources to treat the wounded.
After having to evacuate in late 2006, MSF is now providing medical, obstetrical, and surgical care in Point Pedro, Vavuniya, Kilinochchi, and Mannar.
Conditions Worsen in Eastern Democratic Republic of Congo

Democratic Republic of Congo 2007 © Guillaume Le Duc/MSF
A displaced woman recovers after amputation surgery in MSF’s Rutshuru Hospital in North Kivu province.
The headlines emerging from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) in 2007 paid scant attention to the humanitarian crisis currently unfolding in the eastern province of North Kivu. More than a year after the first democratic elections in decades were supposed to bring stability to this conflict-ridden region, fighting between armed groups has continued in North Kivu.
Supported by MONUC, the UN force, the government is now in open combat with the forces of rebel leader Laurent Nkunda. A number of different groups such as the Mai Mai and the Rwandan Hutu rebels of the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR) are involved in the fighting.
Hundreds of thousands of people have fled their homes in the past year, many of whom have been displaced multiple times. The displaced are often forced to hide in the forest, with little access to food or basic health care and under constant threat of attack from the various armed groups. With few avenues to receive health care, displaced Congolese are increasingly vulnerable to easily treatable diseases and conditions such as malnutrition, malaria, respiratory infections, and obstetrical complications. Outbreaks of cholera have struck Rutshuru and Goma, the provincial capital of North Kivu.
MSF teams have reinforced their activities to try to meet the increasing medical needs, but fighting and insecurity make it difficult for humanitarian workers to deliver assistance to the population. Large areas remain inaccessible, with many roads simply cut off by the insecurity.
One particularly disturbing aspect of DRC's conflict is the alarmingly high rate of sexual violence. In North Kivu, MSF cared for more than 2,375 victims of sexual violence from January through October 2007. In the DRC's Ituri district, the setting of conflict between different armed groups from those operating in North Kivu, 150,000 internally displaced people are still unable to return home. In a state of utter destitution, they remain vulnerable to exploitation and assaults.
Through the Bon Marché hospital in Bunia, capital of the Ituri region, MSF has treated 7,400 rape victims over the last four years. More than one-third of these people were admitted over the last 18 months. MSF also responded this year to a number of disease outbreaks in other provinces, including an epidemic of Ebola hemorrhagic fever in southern West Kasai province.
Living Precariously in Colombia's Conflict Zones

Colombia 2007 © Juan Carlos Tomasi
Graciela and her family are a few of the millions of Colombians who have had to flee their homes to escape fighting between government, rebel, and paramilitary forces.
Largely fuelled by a fight over control of the narcotics trade, Colombia's decades-old civil war often makes headlines, but its impact on the civilian population of the country is rarely the focus of attention.
Over the years, as many as 3.8 million people have been driven from their homes by violence brought on by government troops, paramilitary, and rebel forces battling for territorial control, ranking Colombia third in the world after Sudan and the Democratic Republic of Congo for the largest number of internally displaced people.
Armed groups have a stranglehold on roughly half of Colombia's rural areas, depriving civilians of access to health care by making roads impassable, forcibly conscripting children into militias, and murdering those suspected of collaborating with rivals. These civilians are equally treated with suspicion of potentially “collaborating” with armed groups by Colombia's armed forces and often face harsh reprisals as a result.
In desperation, families flee their homes for urban slums with little more than the clothes on their backs; and when they arrive, looking for work and shelter, they often find conditions that are as threatening as those they fled. Their new homes are overcrowded shacks without adequate facilities. The living conditions can lead to respiratory infections and diarrheal disease, but there is little access to health care. There are also very few internally displaced persons who have the option of returning safely to the homes they were forced to abandon.
MSF has a presence in 13 of Colombia's 32 departments, working in isolated rural areas through mobile and stationary clinics and in urban areas where displaced families have gathered. Teams provide medical care ranging from vaccinations to reproductive care and emergency services, and offer psychological care to victims of violence. As the conflict in Colombia rolls into its sixth decade and armed groups continue to target civilians in their war for control, many Colombians do not remember a time when daily life was not ruled by guns and terror.
Humanitarian Aid Restricted in Myanmar

Myanmar 2006 © Claude Mahoudeau/MSF
A father waits with his son to receive health care at an MSF clinic.
Isolated from the outside world since the ruling military junta came to power in 1962, the people of Myanmar (formerly named Burma) suffer from the consequences of repression and neglect.
The crackdown on monks marching for democracy in September brought international attention to this long-suffering population, but it did not expose what ordinary Burmese go through every day. Faced with high malaria and HIV rates, the impoverished population is provided with little assistance—only 1.4 percent of the regime's budget supports health-care services.
In spite of the overwhelming need, there are few humanitarian aid groups working in the country and, for those on the ground, operating in an independent and impartial manner is difficult. Moreover, donor governments and agencies are reluctant to fund programs that might support the regime. Travel inside the country can require time-consuming visas, which can make responding to emergencies impossible and needs assessments challenging. In some regions, such as those gripped by armed conflict involving Karen and Mon rebels along the eastern border with Thailand, government restrictions have stymied humanitarian aid efforts, including MSF's.
Some of the largest gaps in health services are in the western Rakhine state, where MSF treated 210,000 people for malaria in 2006. Muslims from Rakhine state, known as Rohingyas, live in particularly precarious circumstances. Denied citizenship rights by the state, this group suffers numerous forms of abuse. MSF provides basic medical care and HIV/AIDS treatment to Rohingyas.
The slow response to the country's HIV/AIDS epidemic has fueled the spread of the disease. In Yangon, Rakhine, Kachin, and Shan states, MSF offers comprehensive HIV/AIDS programs, but these meet just a fraction of the need. While there is little independent information to shed light on the number of Burmese in clinical need of life-prolonging antiretroviral (ARV) treatment, of the UN-estimated 360,000 people who are living with HIV, only 10,000 are believed to be receiving ARVs. MSF provides ARV therapy to 8,000 of them. And even fewer have access to care for complicating diseases like tuberculosis. As a result, the UN estimates that 20,000 people die annually from HIV/AIDS.
Civilians Caught Between Armed Groups in Central African Republic

Central African Republic 2007 © Spencer Platt/Getty Images
A mother sits with her child in Massabiou, a village that was attacked by armed militia in April, causing thousands to flee. Those who have returned are now destitute, struggling to survive without food, water, or shelter.
Fighting between government forces and various rebel groups in northern Central African Republic (CAR), which started in late 2005, has caused significant displacement of the population. In the northwest, villages have been attacked, pillaged, and burned, forcing people to flee into the surrounding, inhospitable forest, and severely restricting their access to health care. Civilians are also the victims of violence at the hands of roadside bandits.
In 2007, MSF supported health structures and provided primary and secondary health care in and around Kabo, Batangafo, Paoua, Kaga Bandoro, Markounda, and Boguila in the northwest, and Birao and Gordil in the northeast. In the first eight months of the year, more than 100,000 consultations were carried out and tens of thousands of people—many of them children under five years of age—were treated for malaria and other infectious diseases often associated with poor living conditions.
Acts of harassment and general insecurity frequently forced MSF to stop its mobile clinics on short notice, which sometimes left people without access to health care for up to eight weeks. In June, MSF aid worker Elsa Serfass was shot and killed by rebel gunfire, leading to a lengthy reduction of MSF operations in northwestern CAR. The violence in the northwest has also forced close to 30,000 people into neighboring Cameroon, where they have suffered from a lack of shelter, food, and medical assistance.
During the year, MSF carried out a nutrition intervention after alarming rates of malnutrition were discovered among children within this refugee population. Affected children were treated and MSF also carried out distributions of supplementary food rations. More than 45,000 CAR refugees also gathered in southern Chad, where MSF works in a district hospital and provides assistance to refugees in camps and local residents.
In parts of Vakaga province in northeastern CAR, home to approximately 45,000 people, violence between rebel groups and government troops has forced thousands of people to flee their destroyed homes and villages. Many sought safety in the nearby forest. The region suffers from a near-total lack of health care and MSF provided assistance to the beleaguered population through mobile and fixed clinics in Birao and Gordil.
As Chechen Conflict Ebbs, Critical Humanitarian Needs Still Remain

Chechnya 2007 © Misha Galustov
agency.photographer.ru
Mothers of kidnapped Chechens protest in a park in Grozny.
It has been nearly four years since the most intense fighting subsided between Russian government and rebel forces in the North Caucasus republic of Chechnya. Tens of thousands of internally displaced persons (IDPs), who had fled to the neighboring republics of Ingushetia and Dagestan, have returned to Chechnya. At the same time, reconstruction has increased in the Chechen capital, Grozny, the scene of indiscriminate bombing less than a decade ago, and the republic's airport has been reopened.
Yet the Caucasus region remains highly volatile. Fighting outside Chechnya has increased and a large military presence still inhabits the region. Abductions, disappearances, assassinations, and bombings continue in Ingushetia, North Ossetia, and Dagestan. Inside Chechnya, the security situation is still precarious for civilians. Dangers may range from being caught in the middle of sporadic gunfire to getting into a car accident involving heavy military vehicles, the latter recently having become a common cause of trauma.
Basic health services, particularly in the areas of obstetrical and gynecological care, are woefully lacking and, when available, remain out of reach for many impoverished returnees. Through clinics in and around Grozny, MSF and local Chechen doctors see a population with high levels of chronic illness, including lung, kidney, and cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, the MSF teams also witness widespread needs for psychosocial care, caused by years of exposure to violence and displacement. An MSF survey of IDPs living in temporary accommodation centers in Ingushetia and Chechnya found that nearly all the people interviewed were suffering from anxiety, insomnia, or depression.
Chechnya's wars also took their toll on the republic's tuberculosis (TB) control system. As a result, MSF supports TB hospitals serving a population of 400,000. And many survivors of the wars still need care for crippling injuries. MSF has tried to meet some of this need by operating a reconstructive surgery program in Grozny hospital No. 9 since 2006.
Media Coverage
Listen:
- NPR — All Things Considered
Underreported Humanitarian Crises - WBUR-Boston (NPR) — Here and Now
Underreported Humanitarian Stories - KPCC-Los Angeles (NPR) — AirTalk
Important Humanitarian Stories Of 2007 - KCPW-Salt Lake City (NPR) — Midday Utah
Important Humanitarian Stories Of 2007 - WNYC-New York (NPR) — The Leonard Lopate Show
Underreported: The 10 Most Underreported Humanitarian Stories of 2007 - KZYX-Northern California (NPR,PRI) — Forthright Radio with Joy LeClaire
Top Ten Underreported Humanitarian Stories of 2007
Watch:
Read:
- Sacramento Bee
Editorial: At year's end, a global agenda for compassion



